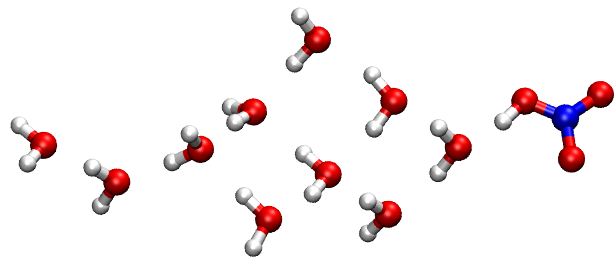
4.6. Example: HNO3 (H2O)10 in Electric Field
Tip
The sample input and output files can be found in testfiles/rigidmol/3-electricfield.
Now you can easily perform a global optimization of the cluster \(\mathrm{HNO}_3\left(\mathrm{H}_2\mathrm{O}\right)_{10}\). Basically, the following two files ef-0.inp and ef-0.cluster are needed:
1ef-0.cluster # cluster file name
230 # population size
350 # maximal generations
43 # scout limit
510.00000000 # amplitude
6ef-0 # save optimized configuration
730 # number of LMs to be saved
12
2hno3.xyz 1
3tip4p.xyz 10
4* 10.0000
After copying misc/charmm/hno3.xyz and misc/charmm/tip4p.xyz to the current path, you can run the global optimization by:
$ rigidmol ef-0.inp > ef-0.out
After a few seconds, You will find the global minimum in ef-0-OPT.xyz and local minima in ef-0-LM.
So, what will \(\mathrm{HNO}_3\left(\mathrm{H}_2\mathrm{O}\right)_{10}\) look like in an electric field, say \(F\) = 0.8 V Å -1? We want to store the results in ef-8*, so first we prepare the input file ef-8.inp which is very similar to ef-0.inp:
1ef-8.cluster # cluster file name
230 # population size
350 # maximal generations
43 # scout limit
510.00000000 # amplitude
6ef-8 # save optimized configuration
730 # number of LMs to be saved
Now prepare ef-8.cluster. You should add the electric field strength in the first line:
12 0.8
2hno3.xyz 1
3tip4p.xyz 10
4* 10.0000
Now you can run the global optimization by:
$ rigidmol ef-8.inp > ef-8.out
Below are the global minima of \(\mathrm{HNO}_3\left(\mathrm{H}_2\mathrm{O}\right)_{10}\) in vacuum and in the static electric field (ef-0-LM/0.xyz and ef-8-LM/0.xyz). Obviously, the electric field elongates the cluster.